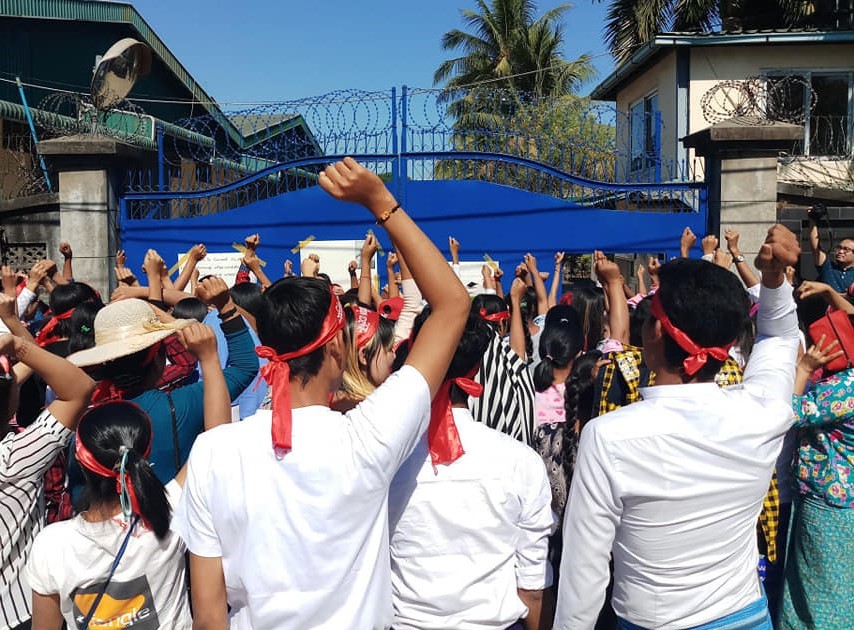
On February 22nd police forces entered the campus of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, heavily beating many students, arresting 31 of them, and teargasing all those present, including teaching staff. Students had taken over the administration building of the University, protesting against a new bill on “Admission in higher education, protection of academic freedom, and upgrading of the academic environment,” according to which a university police force will be introduced. The police were called by the university’s rector, who did not attempt any dialogue with the students, as was the case in similar situations until then.
The newly introduced Law 4777/2021 seems to represent a turning point in Greek political life indicative of a more general shift towards neoliberal authoritarianism during the pandemic. Τhe Covid-19 crisis found Greece severely weakened by ten years of harsh austerity, political upheavals, hopes and disillusionments, and with a right-wing government in power. The latter saw the pandemic as an opportunity to promote its neoliberal agenda and to break down the social contract established in the country after the end of military rule in 1974. The social contract comprised both the solidification of democratic institutions and of the rule of law, and the promotion of a mixed economy of growth through some redistribution, favoring the expansion of the middle-classes.
Contrary to the general orientation of the EU, which recognized the necessity of state services to face the pandemic and thus abandoned strict budgetary discipline, the government of Nea Democratia (ND) pushed all the neoliberal “reforms” that governments implementing the bailout memoranda had not managed (or did not intend) to pass during the last decade. The ND government refused to increase the budget for the national healthcare and education system, public transport, and other relevant services. It also refused substantial financial support to those affected by the lockdowns (small and medium enterprises and their employees), with the exception of big private corporations. Moreover, with citizens locked in their homes, and with the Parliament working under non-regular conditions, the government has been passing a series of laws that initiate long-term structural reforms that will abolish remaining social and labor rights, remove environmental protection in favor of corporate business, promote privatizations of public assets, and attack the public character of education.
Following some global trends, the government has thus opted for a governance model that promotes growing inequalities, shrinking of democratic processes, rule through repression, and absolute media control. Actually, the only sectors heavily subsidized over the past year have been the mass media and the police. In the Greek context, however, there is one more important factor at play. The electoral success of the radical Left twice in 2015, as a result of huge discontent over the years of financial crisis, was a big shock for the Greek Right, which now seems intent to prevent another SYRIZA victory by treating the major opposition party not only as a political adversary but as an enemy whose electoral prospects must be eliminated.
In the context of the breakdown of the post-1974 consensus and intense political antagonism, universities are being used as a spearhead by the Greek Right. This consensus brought about the massive development and democratization of higher education. Universities increased in number, expanded their departments, and received growing numbers of students. They have also been the loci of critical thinking, contestation, political mobilization and emancipation for many young people, as well as a space where the Left often has an intellectual and moral supremacy. It thus comes as no surprise that they are being attacked first.
The Neoliberalization of Higher Education and Law 4777/2021
The efforts to alter the public, free, and open character of Greek universities go back to the 2000s (Angelidou 2017, Gefou-Madianou 2000), when both conservative and social democratic governments made several attempts to waive the financial responsibilities of the state towards universities in order to create a market of lucrative educational services for private investors. In this way, an attempt was made in 2006 to abolish Article 16 of the Constitution, according to which “Higher Education is provided exclusively by public institutions with full self-administration, which are under the supervision of the State”. Such efforts were successfully resisted by intense mobilizations of students and teaching staff. These struggles have substantially delayed, in comparison to other European countries, the implementation of neoliberal policies in higher education over the past two decades: in Greece there are still no tuition fees (with the exception of most Masters’ degrees), university administration remains in the hands of elected representatives, and there is a limited number of private colleges, which lack the prestige of public universities.
However, when Nea Dimokratia came to power in 2019, it targeted higher education by abolishing academic asylum. If the latter is one of the bedrocks of any university in the democratic world, in Greece it has an extra symbolic and political significance, due to its brutal violation by police forces seeking to suppress the student protest movement against the military dictatorship. The most prominent violation took place in November 1973, when a military tank entered the Polytechnic School to crush a student uprising, killing at least 24 students (the exact number has never been officially confirmed) and injuring many more, an event that played a seminal role in the fall of the military regime. As a result, once democracy was restored, police were prohibited by law from entering the university campuses – unless a crime was being committed. However, one of the first laws passed by the ND government abolished the asylum, thus permitting the police to enter the universities. Furthermore, after one year without the physical presence of students and teaching staff in the universities, with escalating prohibitions of public gatherings in the name of the pandemic, and without any real dialogue with the academic community, Law 4777/2021 passed on February 11th. Interestingly, this law was not introduced by the Minister of Education and Religions alone, but together with the Minister of Citizen Protection. The collaboration of these two ministries in educational affairs is unprecedented.
To defend Law 4777/2021, which the academic community overwhelmingly rejects, private and public mainstream media, under the control of the Mitsotakis government, orchestrated an extensive propaganda campaign. The propaganda aimed to discredit universities as centers of lawlessness, disorder, and violence, and their staff as “addicted” and trapped in this situation. In this way, university staff have been portrayed as unable to solve such problems internally, thus requiring external state intervention. A few cases of extremely violent acts against academic authorities and staff, mainly at the universities in the center of Athens, were presented as examples of a generalized situation of criminality and public danger. Also, the media disseminated false reports that the deployment of police corps independent of university administration is a common practice across Europe and the US, and that Greece is just “catching up” with the best practices of the most prestigious academic institutions in the world.
The new law introduces two major changes that threaten academic freedom and university autonomy, as well as the public character of higher education. First, it creates a special corps of 1,030 policemen that will be installed inside the universities and authorized to patrol, arrest, and interrogate whomever they consider to be “disturbing academic life”, a corps accountable not to university authorities but directly to the Chief of the Greek police. Furthermore, fences and checkpoints will be placed at the entrances of each campus, and “Centers for the control and reception of signals and images” will be established, which will have authorization to collect and store information that might infringe on the data privacy of teachers, administrative employees, and students. Furthermore, the law allows for many disciplinary measures to be taken against students and makes teaching staff serve in a disciplinary capacity to judge students’ acts (from plagiarism to the organization of parties, public events, and takeovers inside the campus) and punish them with fines that can go up to their expulsion from the university.
All of these measures are in direct violation of the principle of university self-government, as guaranteed by the Constitution, and have as ultimate goals the subjugation of students and teachers to strict disciplinary measures, and the banning of unionism and political contestation inside universities. It is also scandalous and ironic that in such a ravaged economy, with universities suffering from chronic underfunding, the yearly cost of this special corps will be as much as 20 million euros out of a total of about 90 million euros of yearly funding for all the universities (while an extra 30 million euros will be spent in the first year on control equipment). Moreover, those universities that will not accept police in their campuses will see substantial reductions of their state funding.
The second major change introduced by the law is the application of a system of admission where a minimum of 23% of candidates will be denied entry to public universities. This measure will transfer the cost of these students’ education from the state to their families, as their exclusion will create a pool of students who will turn to private colleges. In November 2020, the same government recognized diplomas by unregulated private colleges to be equivalent to those of public universities. So those candidates who fail the criteria for public universities will be able to enter without any criteria to private colleges, if they can afford the fees. This will lead to the closure of one in every three university departments in the country, affecting mostly peripheral universities. Law 4777/2021 is to be followed in the months to come by another law that will probably replace elected university administrations with nominated ones. The new law will also likely introduce student fees and loans, and the implementation of 3-years diplomas.
The academic community has expressed strong opposition against these neoliberal and authoritarian measurements. It is not fully united, as some academics have supported, and still support, the neoliberalization of higher education over the past two decades. However, there is unanimous recognition of the need for better protection of university campuses, equipment and people – protection that should be controlled by universities and not the police. Staff unions, university councils, rectors, and other academic groups have made concrete propositions for public funding for that purpose – propositions that, unfortunately, the government has now taken into consideration. But protection is something radically different from policing, and it is the latter that provokes strong objections (NoUniPolice 2021). Despite the lockdown and the ban on rallies, thousands of students and teaching staff have demonstrated in Athens and other Greek cities since January 2021, both before and after voting on the law. Moreover, student takeovers are spreading to universities all over the country at this very moment. The law also finds no consent among the majority of elected rectors and councils of the 24 Greek universities, with few exceptions, such as the authorities of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki. Also, numerous university teachers and some of their unions are now planning other means to continue their struggle against the law – for example, seeking to argue in the Supreme Court that several parts of the law are unconstitutional, and exploring possibilities for political disobedience to resist the law’s implementation.
Towards a closed and authoritarian university
The measures introduced with Law 4777/2021 aim to create a closed university, both physically and socially. Physically, by installing fences and control technology that will abolish open access to the campuses. Socially, by restricting the number of students who will have access to higher education, and by transforming the university from a place of sociability and open debate into to a sterilized place where students can only pursue their individual academic and professional paths. The law will definitely not solve any of the existing problems of the universities and it will likely open an era of tension and escalating violence. The brutal police attack at the Aristotle University in February can be seen as a “rehearsal” for such a turn.
More generally, over the past four decades, universities in Greece have been major centers of resistance against the neoliberalisation higher education and society, of critical thinking, and of political activism. They have been privileged places for fostering ideas of social justice and equality. Such critical forces are now faced with the risk of self-restraint, self-censorship, and self-disciplining due to surveillance and the police presence inside university campuses. The establishment of the police inside the universities transgresses democratic principles and transcends the limit of the thinkable until now. Similarly unthinkable until now is PM Kyriakos Mitsotakis’ euphemistic statement in Parliament that, under the new law, “it is not the police that enters the universities, but democracy”. If the state succeeds in passing the “law and order” doctrine and transforming universities into places of fear, surveillance, and repression, while breaking the existing social contract by curtailing the right to free public education, then it will become easier to establish a generalized climate of terror and to ignore social claims and opposition to further restrictions of social rights. If this happens, when the lockdown is over, Greece will be a structurally different country, both in terms of economy and democracy.
Aliki Angelidou is Assistant Professor at the Department of Social Anthropology at Panteion University of Social and Political Sciences, Athens, Greece. Her academic interests include economic anthropology, global economic history, anthropology of Eastern Europe and the Balkans, migration, borders and transnationalism. Currently, she carries out research on household and circular economy in post-memoranda Greece.
References
Angelidou, Aliki 2017. “Anthropology in Greece: Dynamics, Difficulties and Challenges”, in Barrera A., Heintz M. & A. Horolets (eds.), Sociocultural Anthropology and Ethnology in Europe: An Intricate Institutional and Intellectual Landscape, New York, Oxford,Berghahn Books, 250-276.
Gefou-Madianou, Dimitra 2000. “Disciples, Discipline and Reflection: Anthropological Encounters and Trajectories”, in M. Strathern (ed.), Audit Cultures: Anthropological Studies in Accountability, Ethics and Academy. London: Routledge, EASE Series, pp. 256–78.
Initiative of Academics No Police on Campus 2021. “Greek Universities Targeted, Democracy under Threat The New Bill on Higher Education Threatens Academic Freedom and Brings Police Rule on Campuses”, online petition.

Cite as: Angelidou, Aliki. 2021. “’It is not the police that enters the universities, but democracy’: Greek universities as spearhead of an authoritarian turn.” FocaalBlog, 18 March. http://www.focaalblog.com/2021/03/18/aliki-angelidou-it-is-not-the-police-that-enters-the-universities-but-democracy-greek-universities-as-spearhead-of-an-authoritarian-turn/