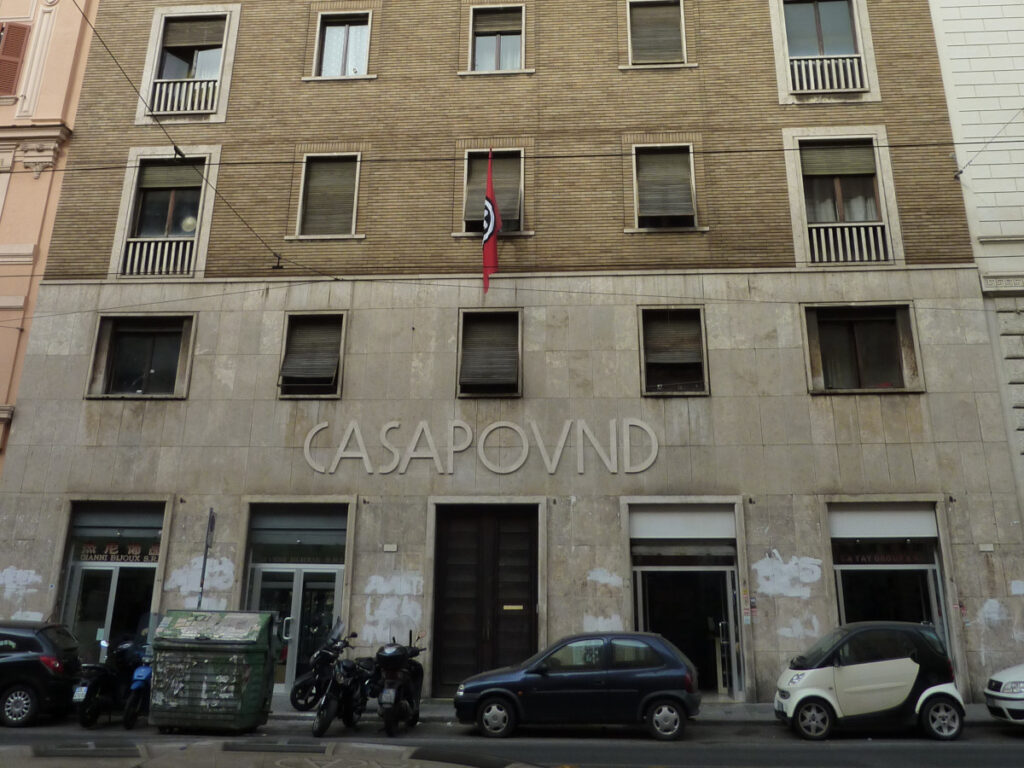
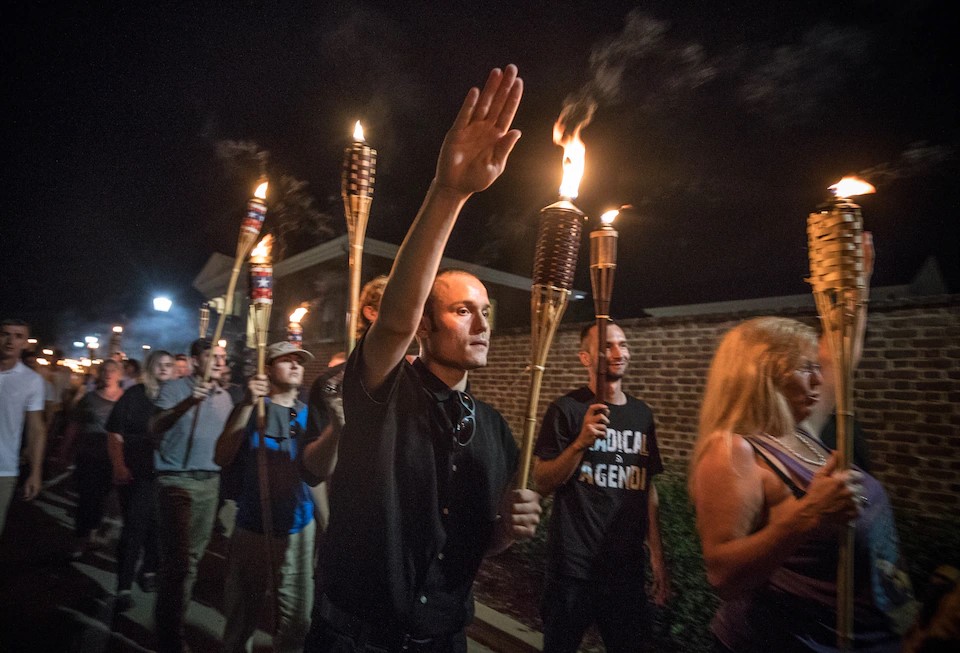It was 2009 when, while living in a squatted house in the Montreuil, a leftist banlieue on the East side of Paris, I was asked how it was possible that there were people occupying buildings in Rome, Italy who self-defined as fascists. The activities of the CasaPound movement were coming to be known on the other side of the Alps as well, and French Leftists were asking me for explanations. Indeed, CasaPound activists used to call themselves third millennium fascists: they have de facto been the first movement to self-claim this label and assert a direct legacy with Fascism since 1945. It is important to remember that Italian law and the country’s constitution prohibit the re-formation of the Fascist party, so a claim of this kind has a certain weight.
Since that moment, I began to focus my research on this subject, first with my PhD dissertation on CasaPound (Cammelli 2015, 2017), and later by continuing to reflect on the place and significance the concept of fascism has been gaining in contemporary European landscapes (within the ERC project F-WORD).
In some ways, the fact that the activists I first engaged were using the label “fascist” to self-identify made things easier for me: my own reproduction of this category in the research was not a choice of political labelling, but simply an act of respecting the emic perspective claimed by the activists themselves. Nonetheless, the specific nature of such a categorization required unpacking.
It is important to recall that, at that time almost 15 years ago, very few people were taking this group seriously as a danger. CasaPound activists were not generally considered new exponents of a fascist-like identity. At an analytical level, it was suggested that I use the “integralist” category proposed by Douglas Holmes (2000) so as to indicate continuity with more traditional political forms, but without the demonizing consequences the label of fascism might trigger. Alternatively, they could be referred to as neo-nationalist, as suggested by Gingrich and Banks (2006) and Kalb and Halmai (Kalb and Halmai 2011) or populist as used by Kalb in his work on Poland (2009). I engaged with this literature to analyze the way this presence was affecting Italian political life, and indeed how cultural identities and political identities seemed to be playing a primary role in absorbing the disappointment experienced by people suffering the double devaluation (Kalb 2022) produced by the social crisis of European modernity – a crisis which, far from being exclusively economic, still continues today.
Almost fifteen years later, we may be in the position to add a few new pieces to the CasaPound puzzle, as the evolution of the political situation in Italy and Europe allows us to make some more specific arguments.
It is evident, as tellingly signalled by the 2022 election of the Meloni government, that the state of affairs once known as the cultural hegemony of the (so-called) left wing in Italy has lost its “momentum”. If there is anything like a cultural hegemony today in the sense outlined by Gramsci, it aligns with the consensus established around the Meloni government and reflects many of CasaPound’s own values. These activists are no longer at the margins; they now find themselves at the centre of the political imaginary of contemporary Italian society (as in other European countries). As confirmed by Douglas Holmes (2019), this not only means that the fascists of today are no longer the violent, skinhead-like people we would have imagined in the past; they have assumed a much more common and widespread profile. It also means that the people who twenty or even ten years ago appeared to be marginal groups of stigmatized militants now play a completely different role in the political arena, having become mainstream and widely accepted. This development may trigger important changes in the way new research on the topic is delineated, and we need to contextualise the rise of right-wing claims and populist nationalist drives more generally within the development of neoliberalism and its irrepressible hegemonic consensus in Europe and the Americas.
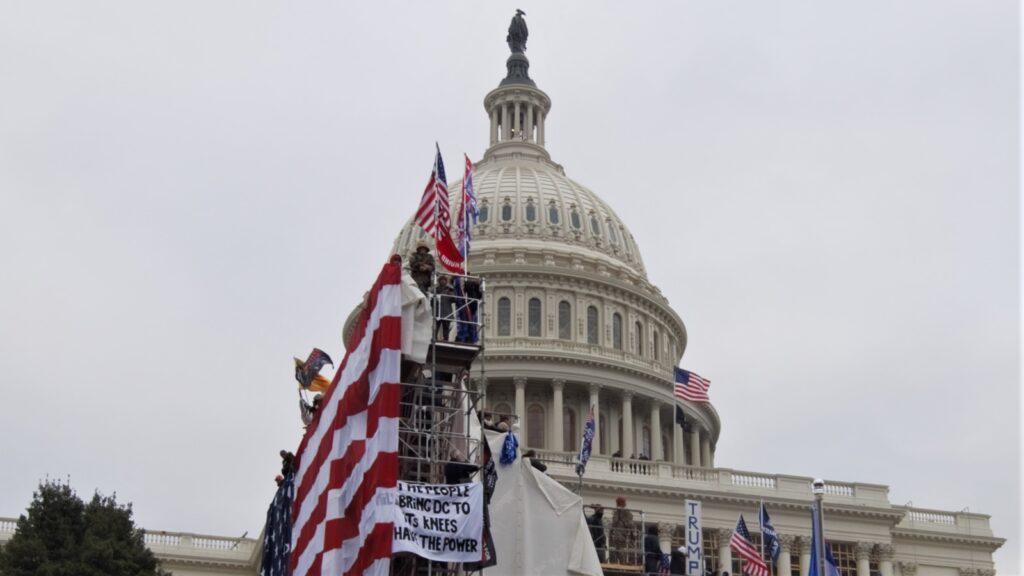
To return to the question of how the concept and word “fascism” are being used, therefore, we may look at the enormous body of literature produced by sociologists and political scientists about political parties and formations positioned on the “right” of the political spectrum. These formations are variously characterised as far-right, extreme-right, radical right or, more recently, populist radical right (Caiani Padoan 2020, Brubaker 2020, Froio et al. 2020, Mudde 2007, 2019). Italian historian Claudio Vercelli recently wrote that, while clearly the past never repeats itself, it is valid to say that the underlying motivations and behaviours evoking an ideological and subcultural substratum with specifically fascist roots does re-emerge (Vercelli 2021: 27). Shortly before (2019), historian Emilio Gentile pointed out the perils of what he calls writing “a-historiography”, that is, the practice of comparing different historical epochs to identify similarities and continuity with the Fascist past; such scholarship, he warns, risks rendering fascism banal and empty. Nonetheless, in view of current political developments in Europe, the USA and beyond, recent literature on EU and US contexts has focused on fascism and faced the f-word head on (Stanley 2018, Traverso 2017, Zetkin Collective 2020). This is not a matter of comparing different historical epochs or making ‘a-historiography’ (Gentile 2019). On the contrary, it is high time for anthropological research to bring its insights to bear on this topic, improving our understanding of the meanings behind the concept of fascism today, its use in social cultural life, and its multiple forms of reception and incorporation.
My argument is that, by silencing the word fascism (using populism, far-right, extreme-right, etc. instead), we risk overlooking the central place historical Fascism plays today as a “mythological machine” (Jesi 2011) and meaning-producer. Silencing this word runs the risk of mis-viewing the central place that the construction of mythological spectacle played historically in the formation of Fascism itself. As Simonetta Falasca Zamponi argues, such spectacle was pursued by using symbols and myths as tools for Fascism to define itself, thus contributing to forging Fascist identity (Falasca Zamponi [1997] 2003: 181). In other words, civic rituals, monuments, and public holidays offered myths and symbols that were instrumental for the self-representation of the nation (Mosse 1975: 145). Mythologies acted to normalise and naturalise meanings, containing them in an apparently permanent space. Historical Fascism used myths and rituals to form/perform a superior spiritual community capable of delineating a cosmology based on (what was asserted as) the natural order of things. Legitimizing the superiority of the virile Fascist man over any other subject, human or non, and with the tools of violence to impose the myth on history, Fascism manifested in history in a deeply pervasive and destructive way. With its future-oriented aspects developed in opposition to the sense of decay characterising the beginning of the last century, it went beyond a simple conservative movement born in reaction to the Bolshevik revolution. Overall, we need to address how memories, rhetoric, and symbols derived from historical Fascism help to constitute new political subjects today, regardless of whether they are ultimately best described as fascists or not (Levi Rothberg 2018: 357). This process is effectively illustrated and concretised by my ethnographic encounter with CasaPound activists (Cammelli 2015, 2017): I found that music and concerts served as gathering sites forging a community of destiny united by faith in the leader and obedience to his will. The community gathered behind this leader become a homogenized collective self, finding significance and reasons for their activism in symbols and images of Mussolini and the Fascist past.
An objective of anthropological investigation should thus be to explore the mythological machine (Jesi 2011) fascism produces of itself, the manifestations that make of this machine that contradictory yet mutable, violent yet meaningful contemporary presence that calls out to be explored in its multiple and differently situated manifestations. Anthropologists should try to find meaning instead of arguing over definitions, to search out lower-case fascism as a heuristic device (Holmes 2019) and violent human reaction to present-day social crises. Nonetheless, fascism is not monstrous, inhuman, or alien in any way. It is a phenomenon wholly entangled with modernity (Bauman 1989) and the way we use reason to justify multiple forms of supremacy.
To conclude, we should consider fascism as it has variously manifested across 1945 and the turn of the millennium, and in its connection with liberalism and the neoliberal turn. And we may need to look more widely around us as well as inside ourselves, not limiting our gaze to some stigmatised militant but instead paying attention to the more general culture of domination and violence that is feeding our contemporary world.
Maddalena Gretel Cammelli is Associate professor in cultural anthropology at the Department Cultures, Politics and Society of the University of Turin, and Principal Investigator of the ERC Starting Grant project The world behind a word. An anthropological exploration of fascist practices and meanings among European youth (F-WORD) (https://fword.unito.it/).
References
Bauman, Zygmunt. [1989] 2010. Modernità e Olocausto. Bologna: Il Mulino.
Brubaker, Rogers. 2020. “Populism and nationalism” in Nation and Nationalism, 26 (1), 2020, pp. 44–66.
Caiani Manuela, Enrico Padoan. 2020. “Setting the scene: filling the gap in Populism studies” In PACO Partecipazione e conflitto 13(1) pp. 1-28.
Cammelli, Maddalena Gretel. 2014. Millenial Fascism. Contribution à une Anthropologie du Fascisme du Troisième Millénaire. PhD diss. Paris: Ecole des Hautes Etudes en Sciences Sociales.
Cammelli, Maddalena Gretel. 2015. Fascisti del Terzo Millennio. Per un’Antropologia di CasaPound. Verona: OmbreCorte.
Cammelli, Maddalena Gretel. 2017. Fascistes du Troisième Millénaire. Un Phénomène Italien? Milan: Editions Mimésis.
Falasca Zamponi, Simonetta. [1997] 2003. Lo spettacolo del fascismo. Soveria Mannelli: Rubettino.
Froio Caterina, Pietro Castelli Gattinara, Giorgia Bulli, Matteo Albanese. 2020. CasaPound Italia. Contemporary Extreme-right Politics. London, New York: Routledge.
Gentile, Emilio. 2019. Chi è Fascista. Bari-Roma: Laterza.
Gingrich, André, Marcus Banks. 2006. Neo-Nationalism in Europe and Beyond. Perspectives from Social Anthropology. New York and Oxford: Berghahn.
Holmes, Douglas R. 2000. Integral Europe. Fast-Capitalism, Multiculturalism, Neofascism. Oxford, Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Holmes, Douglas R. 2019, “Fascism at eye level. The anthropological conundrum”, in Focaal—Journal of Global and Historical Anthropology. 84 pp. 62–90.
Jesi, Furio. 2011. Cultura di destra. Roma: Nottetempo.
Kalb Don, Halmai Gabor (eds). 2011. Headlines of nation, subtexts of class. Working-class populism and the return of the repressed in neoliberal Europe. New York, Oxford: Berghahn.
Kalb, Don. 2009. “Conversations with a Polish Populist: Tracing hidden histories of globalization, class, and dispossession in post-socialism (and beyond)”. American Ethnologist 36(2): 207-223.
Kalb Don. 2022. “Double devaluations: Class, value and the rise of the right in the Global North.” In Journal of Agrarian Change. 23, 1: 204-219.
Levi, Neil, Michael Rothberg. 2018. “Memory studies in a moment of danger: Fascism, post fascism, and the contemporary political imaginary”, in Memory Studies Vol. 11(3) pp. 355–367.
Mosse, George L. 1975. La nazionalizzazione delle masse. Simbolismo politico e movimenti di massa in Germania dalle guerre napoleoniche al Terzo Reich. Bologna: Il Mulino.
Mudde, Cas. 2007. Populist Radical Right in Europe. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Mudde, Cas. 2019. The Far-Right today. Cambridge: Polity Press.
Stanley, Jason. 2018. How fascism works. the politics of us and them. New York: Random House.
Traverso, Enzo. 2017. I nuovi volti del fascismo. Verona: OmbreCorte.
Vercelli Claudio. 2021. Neofascismo in grigio. La destra radicale tra l’Italia e l’Europa. Torino: Einaudi.
Zetkin Collective. 2020. Fascisme Fossile. Paris : La Fabrique éditions.
Cite as: Cammelli, Maddalena Gretel. 2024. “Reflections on contemporary fascism” Focaalblog 9 February. https://www.focaalblog.com/2024/02/09/maddalena-gretel-cammelli-reflections-on-contemporary-fascism/